The wrist does not only comprise of one joint. It, however, encompasses numerous small joints where the forearm and hand bones meet. Pain can happen for several reasons, be it simple fatigue to an underlying issue. Wrist injuries and strained muscles are among the common causes of wrist pain, whilst squeezing the nerves which go through your wrist could also lead to pain.
Wrist pain is discomfort or any pain you feel on your wrist. It is a chronic condition that has various causes. The joint on your wrist plays an enormous role in necessary movements, from writing to texting; hence it can interfere with your day-to-day activities or even impacts the quality of life you live when pain occurs on your wrist.
Here we will explore the causes of wrist pain and the various ways they can be treated.

What are the symptoms of wrist pain?
Pain in the wrist varies depending on its source. One better case is Osteoarthritis, which is frequently depicted to be the same as mild tooth pain, whilst the syndrome known as carpal tunnel results in tingling sensations or feeling of pins and needles, particularly during the night. Also, the specific location of the pain on your wrist can give hints to what is causing your symptom. Apart from the pain, some other symptoms can develop. A wrist sprain, for instance, can lead to bruising and swelling. Some people might develop symptoms like;
Clicking sound while moving the wrist becomes more rigorous after resting periods.
Stiffness is felt all through their wrist and fingers.
Trouble grasping objects becomes uncomfortable for the person in pain.
Symptoms of wrist pain might start as mild and worsen as time goes by. Some pain may occur while doing certain activities, and as the condition worsens, the pain may occur while resting. Also, there are certain times when one can get numb to a point they fail to feel heat or cold.
When do you need to seek medical help?
Not every experience you have with wrist pain needs medical aid. Some minor strains and sprains generally respond to over-the-counter drugs, rest, and ice. However, if the swelling and pain last longer than a couple of days or when it no longer becomes possible to accomplish simple arm movements, you need to get checked by a medical professional. Postponing treatment and diagnosis might result in a decreased range of motion, poor healing, and a long-term disability.
Causes and remedies of wrist pain

1. Carpal tunnel syndrome
One of the three vital nerves in the forearm is the median nerve, which, when compressed or pinched, causes a syndrome called the carpal tunnel. It is positioned on the palm side of your arm and provides sensation to your thumb, middle and index finger, and partly on your ring finger. Also, the median nerve supplies an electrical impulse to the muscle that leads to your thumb. The carpal tunnel consists of structures made up of connective tissues and bones found at the base of your hand. Here, the median nerve gets pinched by irritated or inflamed tendons and other swellings.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can occur on one or both sides of your arm. Apart from causing pain in the wrist, it can lead to weakness, numbness, and a tingling sensation on the side of your hand. The following are the risk factors for the syndrome;
- Pregnancy
- Having medical conditions like underactive thyroid and diabetes
- Performing tasks repeatedly with your hands like drawing, sewing, or typing
- Come from a family with a history of the carpal tunnel since anatomical differences can run in the family.
Common remedies include:
- An analgesic or anti-inflammatory painkillers
- Wrist splints
- Physical therapy
- Resting of your hands and wrists
- Steroid shots

2. Arthritis
Arthritis is another frequent cause of wrist pain, stiffness, and swelling. It makes joints lose the cartilage, which allows them to smoothly move against each other hence, the deterioration of the cartilage leads to pain and swelling of the hand. It often occurs at your thumb’s bottom, the joint nearest your finger’s tip, and your fingers’ middle joint.
There are different types of arthritis, such as Osteoarthritis, which generally occurs with overuse and age. When Osteoarthritis affects your hand, it leads to stiffness, swelling, and pain; infectious arthritis is another type that has symptoms like warmth on the wrist, redness, and a fever that is above 37.7 degrees, and finally, Rheumatoid regularly affects both wrists.
The remedies for arthritis depend on the disability and relentlessness of the pain. If the remedies fail to provide aid, surgery may be recommended as the better option. They, however, include;
- Splints for your wrist or fingers
- Heat
- Analgesics or anti-inflammatory painkillers
- Use FlexiSpot’s ergonomic mouse if you work long hours on your computer
3. Wrist injury
Wrist injuries can also lead to wrist pain. One common way to injure your wrist is by falling and leaning on your hands for support. Disfigured joints on your wrist, bruising, and swelling might be symptoms of a tendon, tendonitis, ligament tear, or a fracture. It is also possible to injure the tissues and nerves around your wrist even though your bones are unharmed. However, if you experience signs like the inability to move your hand, wrist, or finger and deformed joints, you may have a broken bone. Other common wrist injuries include strain, bursitis, and strain. There are numerous types of fractures;
- Simple fracture whereby the bone is stable and aligned
- A complex fracture makes the bone displaced or shifts and more challenging to treat
- Compound. A fracture like this means the bones have broken through the skin
- Comminuted. Here, there is more than one place where the bones are broken
Wrist injury remedies depend on the severity of the injury. You can wear a wrist splint, take a mild pain killer, rest your wrist more or place ice on the affected area for some time to reduce swelling. For fractures, splints or casts can be used to treat simple breaks. Also, you might need wires, plates, or pins to treat the more complicated fractures. In the end, if the injury is so complex, surgery should be recommended.
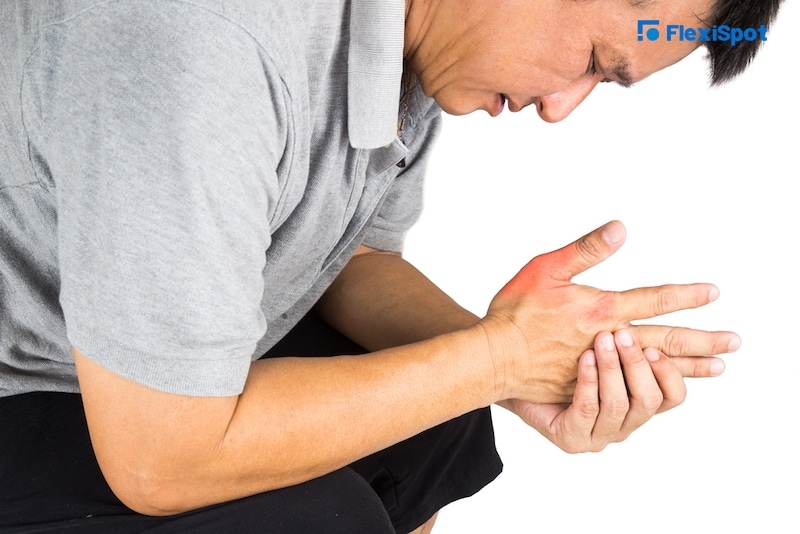

4. Gout
It is inflammatory arthritis that originates from a buildup of uric acid. When food that has organic compounds known as purines is broken down in your body, it produces a chemical known as uric acid. Uric acid gets diffused in the blood and gets out through urine. However, in some instances, the body produces too much uric acid, and in other instances, the body excretes insufficient uric. Excess uric acid is sometimes dumped into the joints, leading to swelling and pain. Pain from gout usually occurs in the wrist, feet, ankles, and knees. The risk factors include;
- Too much alcohol consumption
- Consuming too many drinks and foods with high fructose
- Obesity and conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and kidney disease
- We are eating foods rich in purine, such as red meat
The remedies for gout consist of:
- Drinking more water to reduce the uric acid concentration
- Taking the prescribed medicine to reduce uric acid
- Cutting back on foods rich in fats and alcohol
- Using anti-inflammatory drugs like naproxen and ibuprofen

5. Trigger finger
It is sometimes called stenosing tenosynovitis. It makes the thumb or fingers lock in a bent manner. It is painful, particularly when you straighten or bend the thumb or finger that is affected. This condition develops after the flexor tendons that control thumb and finger movements become irritated, making them thicken inside the tendon sheath surrounding flexor tendons. It makes the movement of tendons so complicated as, in the end, the tendon becomes stuck while trying to straighten your wrist.
The remedy includes resting, wearing a splint, and using over-the-counter drugs. Also, corticosteroid injections can help relieve the pain and symptoms, and if the treatment fails, surgery might be the best option.
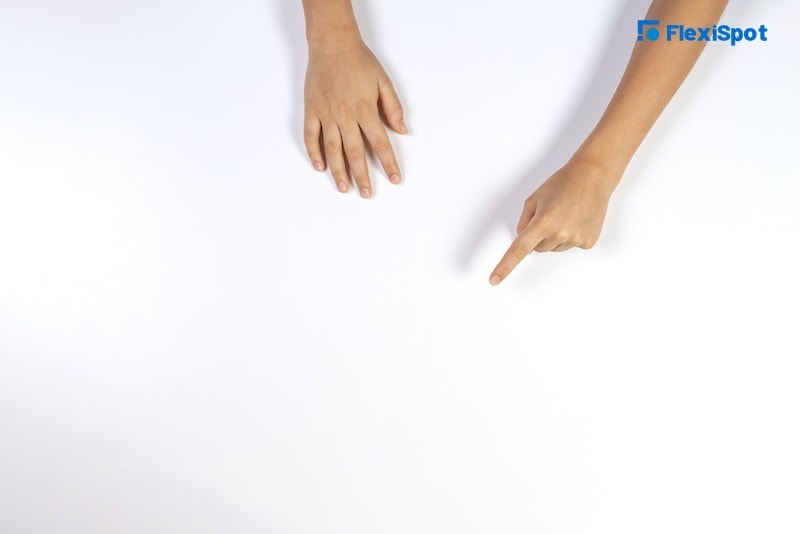

Exercises that can help reduce pain on the wrists.
If your wrists are painful from overworking them, you can do uncomplicated exercises that can help you ease the tension and stiffness. If you already have been diagnosed with conditions that affect your wrist, like carpal tunnel, consult your doctor before trying the exercises.
Wrist deviation. Rest your forearm on the board with your hand padding under your wrist and hanging off. Let your thumb face upward and move your hand up and down as though you are waving.
Wrist extension and flexes. Place your forearm on a board with fabric padding under your wrist. Place your arm in a position that makes your arms face down, then move your hand until you feel a gentle stretch. Take it back to its original position and repeat the procedure.
You can use FlexiSpot’s height adjustable desk to position your forearm in a way that is parallel to the floor to avoid wrist pain. You can also use a bean bag or wrist rest in front of your keyboard to reduce the pressure on your wrist. Pick FlexiSpot pointers to avoid wrist pain and have a healthy life.